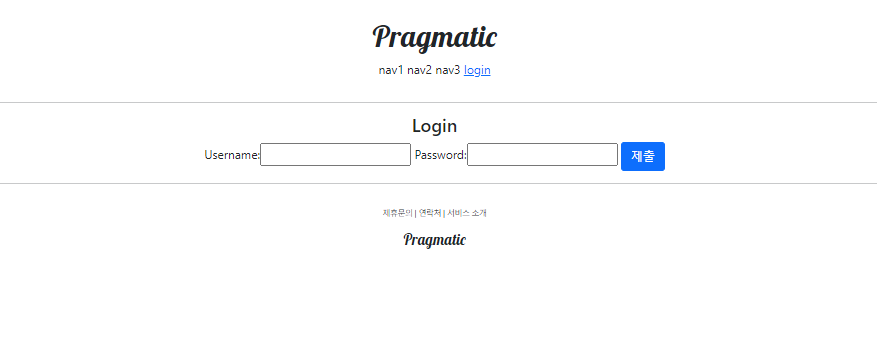
바로 접속해서 로그인

로그인 성공
22강 Login / Logout 구현
로그인 후 어카운트 프로필로 간다. 기본적으로 설정되는곳
메카니즘 login view, logout view -> redirect
next -> login_redirect_url->default(profile)
으로 간다. 순서이다. 그렇다.
로그인할때마다 이제 .. login이렇게 입력할텐데
창을 만들어줍니다.
앵커태그를이용하여 한페지이내에 링크를 만들어준다.
span 태그란 ?
글씨가 가로로 펼쳐짐
줄바꿈은 옆으로 펼쳐짐
<span>태그는 inline element (인라인 엘리먼트)라 자신의 content 만큼 공간을 차지한다.
div태그란?
글씨를 한 박스안에 묶음
줄바꿈은 아래로 펼쳐짐
코드의 행 전체를 차지한다.
만약 코드가 1,000줄이 넘고 코드도 다른 코드 30개들이 있는데 여기에 모두 동일한 효과를 적용시켜야 된다고 하면,
코드 하나하나에 효과를 넣는 게 아니라 <div> 태그로 묶어 나중에 css로
30여 개의 코드에 동일한 효과를 적용시킬 때 사용한다.
setting.py
"""
Django settings for pragmatic project.
Generated by 'django-admin startproject' using Django 3.2.6.
For more information on this file, see
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.2/topics/settings/
For the full list of settings and their values, see
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.2/ref/settings/
"""
from pathlib import Path
import os, environ
from django.urls import reverse_lazy
env = environ.Env(
# set casting, default value
DEBUG=(bool, False)
)
# Build paths inside the project like this: BASE_DIR / 'subdir'.
BASE_DIR = Path(__file__).resolve().parent.parent
# reading .env file
environ.Env.read_env(
env_file= os.path.join(BASE_DIR, '.env')
)
# Quick-start development settings - unsuitable for production
# See https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.2/howto/deployment/checklist/
# SECURITY WARNING: keep the secret key used in production secret!
SECRET_KEY = env('SECRET_KEY')
# SECURITY WARNING: don't run with debug turned on in production!
DEBUG = True
ALLOWED_HOSTS = []
# Application definition
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'accountapp',
]
MIDDLEWARE = [
'django.middleware.security.SecurityMiddleware',
'django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware',
'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware',
'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',
'django.contrib.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware',
'django.contrib.messages.middleware.MessageMiddleware',
'django.middleware.clickjacking.XFrameOptionsMiddleware',
]
ROOT_URLCONF = 'pragmatic.urls'
TEMPLATES = [
{
'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')],
'APP_DIRS': True,
'OPTIONS': {
'context_processors': [
'django.template.context_processors.debug',
'django.template.context_processors.request',
'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth',
'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages',
],
},
},
]
WSGI_APPLICATION = 'pragmatic.wsgi.application'
# Database
# https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.2/ref/settings/#databases
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.sqlite3',
'NAME': BASE_DIR / 'db.sqlite3',
}
}
# Password validation
# https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.2/ref/settings/#auth-password-validators
AUTH_PASSWORD_VALIDATORS = [
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.UserAttributeSimilarityValidator',
},
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.MinimumLengthValidator',
},
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.CommonPasswordValidator',
},
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.NumericPasswordValidator',
},
]
# Internationalization
# https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.2/topics/i18n/
LANGUAGE_CODE = 'en-us'
TIME_ZONE = 'UTC'
USE_I18N = True
USE_L10N = True
USE_TZ = True
# Static files (CSS, JavaScript, Images)
# https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.2/howto/static-files/
STATIC_URL = '/static/'
STATIC_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'staticfiles')
STATICFILES_DIRS = [
BASE_DIR / "static",
'/var/www/static/',
]
# Default primary key field type
# https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.2/ref/settings/#default-auto-field
DEFAULT_AUTO_FIELD = 'django.db.models.BigAutoField'
LOGIN_REDIRECT_URL = reverse_lazy('accountapp:hello_world')
LOGOUT_REDIRECT_URL = reverse_lazy('accountapp:login')
로그인에서 접속했을 때 헬로월드를 보여주고 로그아웃을 했을 때 로그인창을 보여준다.
login.html
{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block content %}
<div style="text-align: center">
<div>
<h4>Login</h4>
</div>
<div>
<form action="" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
{{ form }}
<input type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">
</form>
</div>
</div>
{% endblock %}
urls.py
from django.contrib.auth.views import LoginView, LogoutView
from django.urls import path
from accountapp.views import hello_world, AccountCreateView
app_name = 'accountapp'
#"127.0.0.1:8000/account"
#왜 어카운트앱안에 있는데 또 다시 만드냐
#저위에 라우트를 매번 쓸수 없기에 기능을 사용해서 헬로월드라는 곳으로 바로가라는 함수를
#사용할 수 있다.
urlpatterns = [
path('hello_world/', hello_world, name='hello_world'),
#롸우터의 이름
path('login/', LoginView.as_view(template_name='accountapp/login.html'), name='login'),
path('logout/', LogoutView.as_view(), name='logout'),
path('create/', AccountCreateView.as_view(), name='create'),
]
views.py
from django.contrib.auth.forms import UserCreationForm
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
from django.http import HttpResponse, HttpResponseRedirect
from django.shortcuts import render
# Create your views here.
#view 단의 완성
from django.urls import reverse, reverse_lazy
from django.views.generic import CreateView
from accountapp.models import HelloWorld
def hello_world(request):
if request.method == "POST":
# 포스트가 완료한이후에 겟으로 되돌아가서 남아있는 글들을 지울 수 있게한다.
temp = request.POST.get("hello_world_input")
new_hello_world = HelloWorld()
new_hello_world.text = temp
new_hello_world.save()
hello_world_list = HelloWorld.objects.all() #헬로월드에 모든 데이터를 다 긁어온다.
return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('accountapp:hello_world'))
# 포스트가 완료한이후에 겟으로 되돌아가서 남아있는 글들을 지울 수 있게한다. redirect
# URL에서 ACCOUNT를 가져온다. 해당 경로를 만들어줄 함수를 쓴다
else:
hello_world_list = HelloWorld.objects.all()
return render(request, 'accountapp/hello_world.html',
context={'hello_world_list': hello_world_list})
#view는 만들었고 이제 route해줘야한다.
#특정 주소를 만들어 주는 작업이 필요하다.
class AccountCreateView(CreateView):
model = User
form_class = UserCreationForm
success_url = reverse_lazy('accountapp:hello_world') #여기서 reverse를 사용불가 클래스형
#reverse는 함수형에서 사용한다.
template_name = 'accountapp/create.html'
header.html
<div class="pragmatic_header">
<div>
<h1 class="pragmatic_logo">Pragmatic</h1>
</div>
<div>
<span>nav1</span>
<span>nav2</span>
<span>nav3</span>
{% if not user.is_authenticated %}
<a href="{% url 'accountapp:login'%}?next={{ request.path }}">
<span>login</span>
</a>
{% else %}
<a href="{% url 'accountapp:logout'%}?next={{ request.path }}">
<span>logout</span>
</a>
{% endif %}
</div>
</div>
'Computer Science > Django_pinterest' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 210821 장고 25커밋, UpdateView를 이용한 비밀번호 변경 구현 (0) | 2021.08.21 |
|---|---|
| 210820 장고 23강 Bootstrap 을 이용한 Form 디자인 정리 (0) | 2021.08.21 |
| 210820 장고 21강 CreateView를 통한 회원가입 구현 (0) | 2021.08.20 |
| 210819 장고 20강 CRUD 소개 (0) | 2021.08.19 |
| 210819 장고 19강 디버깅 (0) | 2021.08.19 |


